Welcome to the Learning Resource Center for WATER. Listed below are some key questions that you are probably asking yourself. Take the time to glance through these questions to find more information about improving the water in your home or business.
WATER TREATMENT
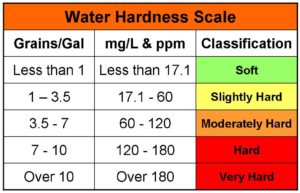
What is hard water?
Hard water is a common quality of water which contains dissolved compounds of calcium and magnesium and, sometimes, other divalent and trivalent metallic elements. The term hardness was originally applied to waters that were hard to wash in, referring to the soap wasting properties of hard water. Hardness prevents soap from lathering by causing the development of an insoluble curdy precipitate in the water; hardness typically causes the buildup of hardness scale (such as seen in cooking pans). Dissolved calcium and magnesium salts are primarily responsible for most scaling in pipes and water heaters and cause numerous problems in laundry, kitchen, and bath. Hardness is usually expressed in grains per gallon (or ppm) as calcium carbonate equivalent.
The degree of hardness standard as established by the American Society of Agricultural Engineers (S-339) and the Water Quality Association (WQA) is as follows:
How does a water softener work?
A water softener is installed where the water enters the house. It removes calcium (hardness) and magnesium from the water and exchanges it for sodium or potassium, depending upon which type of chloride you use.
Can a Water Softener save me money?
The answer is yes. By preventing the scale buildup on heat exchange surfaces, the energy (and fuel) needed to heat water is maintained. Lime scale insulates the heating surface causing more energy to be used to bring water to temperature. Further, the water saving is realized by not running the tap until that water comes to temperature. Further, soft water makes more effective use of soaps and cleaning chemicals to be effective utility water (for washing and cleaning).
How much maintenance does a water conditioner require?
Water softeners are self-cleaning. Some automatically measure the amount of water used and regenerate by back flushing and running salt brine through the system to remove the minerals collected. You add salt once a month. Like a vehicle, it is a good idea to service on an annual basis
What is reverse osmosis? Sometimes shortened to the acronym RO, these systems force water, under pressure, into a module that contains a semipermeable membrane and a number of other filtration steps. A typical RO system has a pre-filter designed to capture larger particles, chlorine, and other substances; a semipermeable membrane that captures more contaminants; an activated carbon filter that removes residual taste, odor, and some organic contaminants; and a storage tank to hold the treated water for use.
What is an ultraviolet system? How does it work? An ultraviolet (UV) system uses UV to inactivate certain bacteria, viruses and cysts that may be present in the water source that flows through the systems UV chamber. The effectiveness of UV depends upon the dose of disinfectant received by the organism, which is the combination of UV intensity times the contact time involved. It is advisable to always pre-treat the water entering the UV system.
What is a Backwashing Filter?
A backwashing filter is a tank with a specific filtration media filled inside, additional components for structure, and a control valve. The media is typically specific to the elements or components that need to be filtered from the water, such as but not limited to; Arsenic, Nitrates, Iron, Manganese, Chemicals, and Sediments. The water enters the tank, and the elements or components are stopped by the filtration media. The water then travels downwards and travels up through a stem at the bottom of the tank entering the household. During the backwash cleaning cycle, the control valve adjusts the pressure and water flow in the reverse direction, thereby purging the collected elements into a designated drain.
Does my water treatment systems need to be certified?
Health Canada recommends that all products that come into contact with drinking water be certified to the appropriate health–based performance standard developed by NSF International. In the case of water softeners, it is recommended that they be certified as meeting standard NSF/ANSI 44. Components employed in conjunction with the water softener (e.g. filters) should also be certified to meet other applicable NSF/ANSI Standards. These standards have been designed to safeguard drinking water by helping to ensure material safety and performance of water softeners that come into contact with drinking water. In Canada, CSA International, NSF International, QAI, IAPMO and Underwriters Laboratories have been accredited by the Standards Council of Canada to certify drinking water materials as meeting the above–mentioned standards. All of our products are certified.
How often does the UV light bulb (lamp) need to be replaced?
The ability of the lamp to emit UV light decreases over time. You should change the UV lamp annually. Remember – UV light is invisible! Even though the lamp is still glowing after one year, there might not be enough UV light reaching your water to be effective.
Can chlorine in my bath water cause my skin to be itchy and my hair brittle?
Yes. Many people experience this type of skin reaction to chlorine in their bath water. A simple carbon filter shower filter will remove it as well as a whole house carbon filter, which would remove all the chlorine throughout the house
What is the best way to have water tested?
Contact us to schedule a FREE in-home water test so we can identify your water problems and determine the right water solution for your home.
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) water filtration is the best water purification method available. Commonly used by premium bottled water companies, it is effective in eliminating or substantially reducing a wide range of contaminants. Of all methods used to treat residential drinking water, reverse osmosis has the greatest range of contaminant removal as it will remove particles as small as individual ions. The pores in a reverse osmosis membrane are approximately 0.0005 micron in size. When compared to the size of bacteria at 0.2 to 1 micron & viruses at 0.02 to 0.4 microns, you can see the reverse osmosis is highly effective at purifying both municipal and well water.
How Reverse Osmosis (RO) works?
Reverse osmosis uses a semi-permeable membrane, allowing pure water to pass through it, while rejecting the contaminants that are too large to pass through the tiny pores in the membrane. Quality reverse osmosis systems use a process known as crossflow to allow the membrane to continually clean itself. As some of the fluid passes through the membrane the rest continues downstream, sweeping the rejected contaminants away from the membrane and down the drain. The process of reverse osmosis requires a driving force to push the fluid through the membrane (the pressure provided by a standard residential water system is sufficient -+40 psi).
